Resource Library
Any CA4SH partner can submit a resource to the Library, where we hope to increase visibility of diverse work related to improving soil health globally.
Please send a web link or a file to communications@coalitionforsoilhealth.org if you would like to submit a resource.
Economic Impact of Integrated Soil FertilityManagement on Smallholder Farmers' Income
ISFM significantly increases farm income, with an average net income increase of 80%, and wheat being the most profitable crop. However, income variability persists as some farmers face low or negative net return when labour costs are accounted for. Adoption is also hindered by limited input access, credit constraints and labour shortage. Methodological limitations, including data issues and spillover effects, suggest caution in generalizing findings. Further research is needed to refine insights in regional and crop-specific dynamics. The findings highlight ISFM’s significant impact on smallholder income, reinforcing its potential for sustainable agricultural development in the Ethiopian highlands.
CoMADI | Community Managed Agricultural Development Initiative forSustainability and Community Empowerment
The local government's efforts in the Amhara region to combat land degradation and food insecurity are commendable, especially with the positive outcomes seen in rehabilitated lands and increased agricultural productivity. However, the challenges you've highlighted regarding the government's top-down approach are significant. The high staff turnover, understaffing, and limited functionality of key committees hinder effective project management and slow down implementation. Moreover, issues with the delivery of inputs, as well as reduced community participation and ownership, raise important questions about transparency and accountability.
Small Scale Mechanisation in Tigray: Gender Sensitive Approaches for Climate Change Mitigation
In the Tigray region of Ethiopia, agriculture is transformed through small-scale mechanization. In the Emba Alaje district, the Dellet Agricultural Mechanization Youth Group has been providing Mechanization services with twowheel tractors to the local community. Since 2021, the group has been supported by the Integrated Soil Fertility Management Project and CIMMYT through trainings and the provision of accessories for their tractors. By modernizing traditional farming methods, which relied on animal and human power, they help local farmers increase productivity, reduce labour, and adapt to climate change. This shift not only boosts agricultural output but also contributes to higher incomes and better livelihoods for smallholder farmers in the region.
Application of ISFM Technologies Survey Report
Agriculture is the primary economic activity in Ethiopia, with the majority of the population engaged in farming. However, food security remains a significant challenge, largely due to issues such as soil degradation and low fertility. Addressing soil fertility is essential for improving the livelihoods of Ethiopian farmers.To tackle this issue, the Integrated Soil Fertility Management (ISFM+) project promotes a set of integrated soil fertility management (ISFM) technologies and emphasizes peer learning and participatory approaches to enhance the effectiveness of these interventions. This report presents the findings of a 2024 survey aimed at tracking the dissemination, application, and adoption of ISFM technologies by smallholder farmers in the project’s intervention areas.
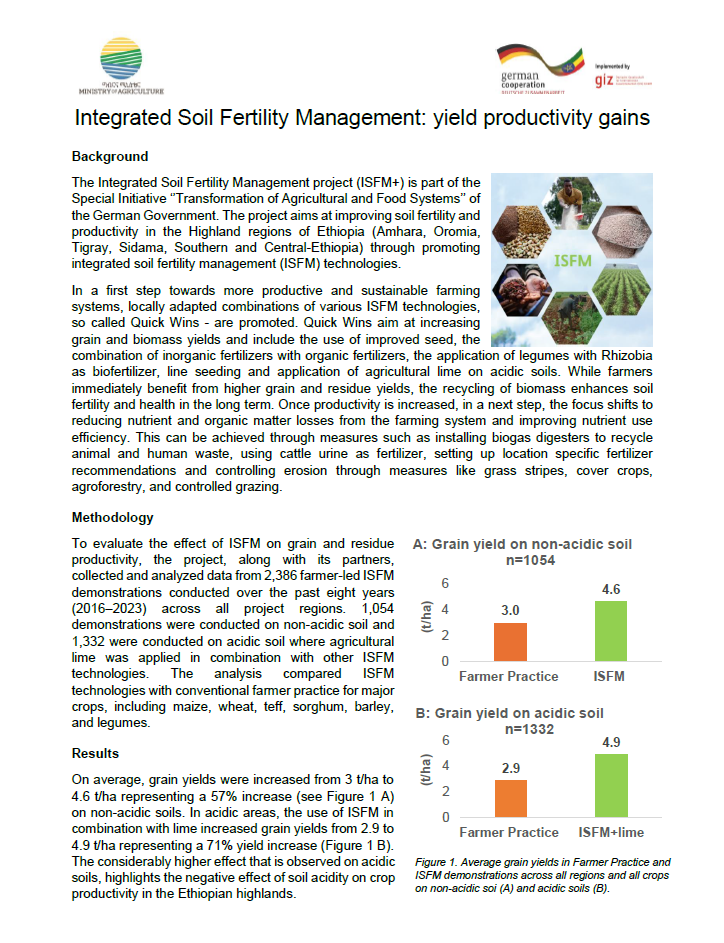
Integrated Soil Fertility Management: Yield Productivity Gains
The Integrated Soil Fertility Management project (ISFM+) is part of the Special Initiative ‘’Transformation of Agricultural and Food Systems’’ of the German Government. The project aims at improving soil fertility and productivity in the Highland regions of Ethiopia (Amhara, Oromia, Tigray, Sidama, Southern and Central-Ethiopia) through promoting integrated soil fertility management (ISFM) technologies.
NOAH | Micro-gasifier cookstoves
➢ Local production of stoves and fuel started
➢ Fuel from waste and sustainably grown wood from agroforestry plantations
➢ Establishment of 4 workshops per year
➢ 50 jobs per workshop
➢ biochar from households is used for biochar-compost production (carbon removal)
Mechanization | Beating time poverty of rural women in Ethiopia as enabler for equitable development
Women suffer disproportionally from time poverty, often spending 16 h a day working. This severely limits their possibilities to participate in capacity building (reach) or to implement measures (benefit) as well as their ability to participate and advocate in decision-making processes (empower).
An anthropological study revealed that farm work such as planting, processing, threshing/shelling and weeding consume much of their time. Also fetching water is a huge challenge. Women headed households are also unable to plough their fields without support by male relative and are therefore often disowned of their property or its economic use. Moreover, unequal access to resources exacerbates these challenges, hindering women from realizing their full potential in the agricultural sector.
Some of these constrains can be addressed by the broad deployment of small-scale mechanization options. Two-wheel tractors operated by local service providers have been shown to be in great demand especially by women.
Implementing agroecology through soil protection
Agroecology is an integrated and holistic approach to sustainable agricultural and food systems, from production to consumption. It is pursued in three dimensions: science, agricultural practices, and a social movement. The 13 agroecological principles of the HLPE (2019) provide guidance for its implementation.
Soil health and crop nutrient management: Building resilience and increasing the efficiency of nutrient application
Soil health is fundamental for the productivity of cropping systems. It relies on three interlinked pillars: (1) availability of sufficient nutrients, (2) organic matter and (3) soil biota. Organic matter regulates pH and supports nutrient availability, water retention and soil biodiversity. Soil biotas decompose organic matter and improve soil structure by forming soil aggregates.
Guidebook for Project developers: Best practice for Agricultural carbon project development targeting Voluntary Carbon Markets (VCM)
This guidebook aims to inform the design of agricultural carbon projects and to support project developers in navigating key project development issues, drawing on lessons learnt from a pilot project; the Western Kenya Soil Carbon Project (WKCP) as well as feasibility studies in India and Madagascar.
Gender in Soil Matters: Comparative Insights from Multi-Country Gender Analyses
This synthesis report examines how gender is implicated in soil health interventions across diverse country contexts, and how Soil Matters as a global programme can respond with both gender-responsive and gender-transformative approaches. It draws on national gender analyses conducted between 2024–2025, offering cross-country insights, strategic recommendations, and key entry points to ensure that gender equality is not only acknowledged but actively pursued within the programme’s design, delivery, and scaling pathways.nger. Depending on the climate scenario, up to 80 million additional people could be at risk of hunger due to climate change (IPCC 2022).
Soil Protection and climate change adaptation: How can a healthy soil help combat the impacts of climate change?
Climate change is a major threat to agricultural production. Africa is particularly affected. Since 1961, total agricultural productivity growth in Africa has been reduced by 34 per cent due to climate change. These negative effects are likely to increase. The yields of staple cereals and legumes in the tropics are expected to decline by 5 per cent for every degree Celsius of global warming. Yield reductions and harvest failures are undermining food security and increasing hunger. Depending on the climate scenario, up to 80 million additional people could be at risk of hunger due to climate change (IPCC 2022).
Sowing Sustainability: Agroecology and Sustainable Land Management in Synergy
This compilation consists of ten selected SLM practices that contribute to improved soil fertility and enhance soil health for the sustainability of food and agricultural systems.
Fields of Harmony: Pulses and Sustainable Land Management
This compilation consists of ten selected SLM practices that contribute to improved soil fertility and enhance soil health for the sustainability of food and agricultural systems.
Harvesting Tomorrow: Advancing Sustainable Land Management for Soil Fertility
This compilation consists of ten selected SLM practices that contribute to improved soil fertility and enhance soil health for the sustainability of food and agricultural systems.
Soil protection and reduction of greenhouse gas emissions: How can a healthy soil contribute to climate change mitigation?
Climate change poses a threat to global agriculture, with the African continent particularly vulnerable. Since 1961, climate change has reduced agricultural productivity in Africa by 34 per cent. Projections warn that up to 80 million additional people could be affected by hunger. Already today, 40 per cent of the world’s land area is considered degraded. At the same time, agricultural activities contribute considerably to the degradation of ecological and agricultural systems.
Soil protection – a trigger for the transformation towards sustainable agricultural and food systems
Agricultural and food (in short here agrifood) systems encompass the entire value chain of food and agricultural production, from seed selection and crop cultivation to storage, transport, processing, marketing, consumption, and waste management. These systems are shaped by social, economic, and policy factors.
Nurturing the Earth: The Role of Soil Protection and Rehabilitation for Food Security
The main objective of this study is to analyse the existing studies and sources in order to compile and prepare evidence on the link between ProSoil’s actions on food security in a communicative way key messages) for communication purposes and for accountability of the commissioning party and co-funders. Accordingly, conclusions and key messages are presented in chapter 5.